Panorama

The Panorama test is currently one of the world's most reliable, safe and accurate non-invasive chromosomal disease screening tests based on DNA single nucleotide polymorphism research, which can be performed from the ninth week of pregnancy. The purpose of the Panorama test is to screen the fetus for Down, Edwards, Patau, Turner, Klinefelter, Jacobs syndrome, as well as high-risk pregnancies for monosomy X and triploidy.
What is the significance of the Panorama test, and how does it work?
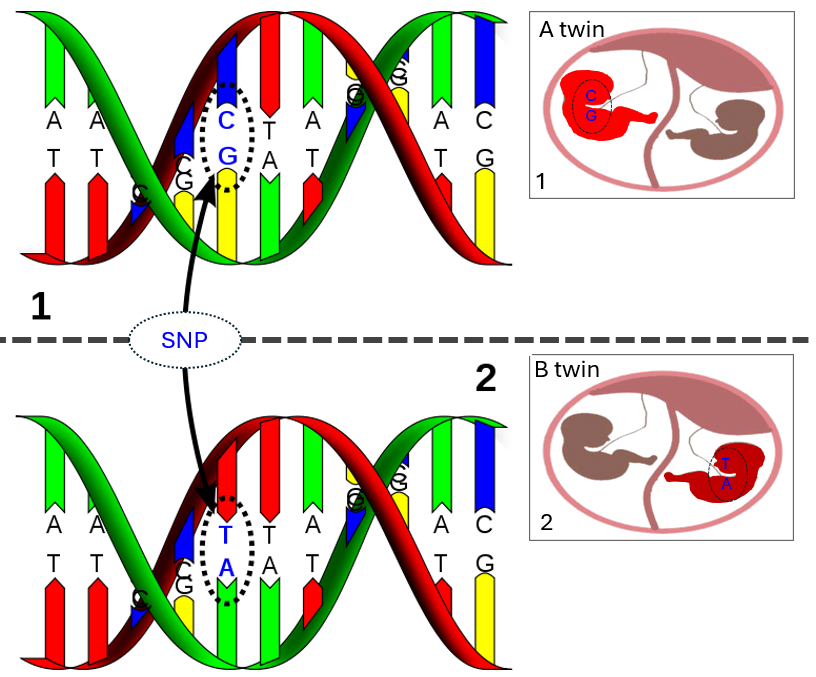
The human chromosome consists of 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome contains 1000-3000 genes, which in turn consist of nucleotides or bases (A-adenine, T-thymine, C-cytosine, and G-guanine). Individual differences in the nucleotide sequence exist. The difference of one nucleotide in the gene sequence of two different people is called single nucleotide polymorphism (single nucleotide polymorphism—SNP).
Identical twins have identical chromosomes, but if one identical twin has a C-nucleotide at a certain position in the DNA chain, the other identical twin may have a T-nucleotide in the same position. This method allows us to distinguish identical twins from each other.
The Panorama test is performed from the mother's blood sample, containing maternal and fetal DNA (genetic material). The fetal DNA to be tested comes from the placenta. This extracellular DNA carries the genetic information of the child. Panorama uses the NATUS methodology, which examines SNPs in extracellular DNA as markers to distinguish fetal and maternal DNA. Next, gene chip technology is used, where 19,500 SNPs are analyzed simultaneously. This provides reference points for all fetal extracellular DNA and assesses whether or not the fetus has the chromosomal disorder sought. The sex of the fetus can also be determined with this test.
The Panorama test, a non-invasive prenatal screening test, is a secure choice for you and your baby. It involves only a blood sample taken from your arm, which is then sent by express courier to the Natera laboratory in San Carlos, USA.
What does the Panorama test tell me?
In singleton pregnancies, the pregnancy is analyzed for trisomy 21, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, monosomy X and triploidy. Sex chromosomes (XXY, XXX and XYY) will be notified when identified.
In twin pregnancies, the pregnancy is evaluated for zygosity. A zygosity test determines whether twins are monozygotic (identical) or dizygotic (non-identical). Depending on the zygosity, different chromosomal abnormalities are analyzed.
For monozygotic (identical) twins, the pregnancy is analyzed for trisomy 21, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, monosomy X and triploidy. Sex chromosomes (XXY, XXX and XYY) will be notified when identified.
In dizygotic (non-identical) twins, the pregnancy is only tested for trisomy 21, trisomy 18 and trisomy 13.
A singleton pregnancy achieved with the help of an egg donor or surrogate is only analyzed for trisomy 21, trisomy 18 and trisomy 13.
How reliable is the Panorama test?
This screening test can detect over 99% of chromosome 21, 18 and 13 abnormalities and about 92% of monosomy X cases. The need to repeat the test due to an unclear result is less than 1%.
What are the alternatives to the Panorama test?
While the Panorama test is a valuable screening tool for chromosomal disorders, it has its limitations. It cannot detect fetal microdeletions, assess the anatomical structures of the fetus, or predict complications like preeclampsia and fetal growth retardation. This underscores the importance of considering other testing options.
If you also want information about fetal microdeletions, you may be interested in the Panorama 22q11 test and the Panorama XP test.
If you're seeking a more comprehensive understanding of fetal health, the Fetal Double test is a viable option. It covers fetal chromosome pathologies, microdeletions, the development of fetal organ structures, and potential pregnancy complications. The Fetal Double test includes the KaryoPlus test, the OSCAR test, and the GeneSafe Complete test, offering a thorough assessment of fetal health.
If you're interested in learning about a wide range of genetic diseases, including those inherited from parents, the Fetal Triple test is a comprehensive option. It includes the KaryoPlus test, the OSCAR test, and the GeneScreen Complete test, in addition to the GeneSafe Complete test, providing a thorough understanding of your baby's genetic health.
In the case of women whose ultrasound examination remains suspicious of a fetal malformation, invasive diagnostic tests such as chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis are used, which detect more than 99% of all chromosomal abnormalities, including rare chromosomal abnormalities that cannot be detected by the Panorama test or other screening tests. In the case of diagnostic studies, it is only necessary to take into account that in 0.1% of cases, they can cause a miscarriage, regardless of whether the fetus has a chromosomal pathology or not.
When will I know the result of my test?
You will find out the test results 14 working days after the blood test.
What results can I expect from the Panorama test?
- LOW RISK
A low-risk screening result means that your fetus has not been diagnosed with chromosomal disorders that the Panorama test can investigate.
- HIGH RISK
A positive screening result means that your fetus is highly likely to have one of the chromosomal diseases detected by the PAnorama test, but it is not 100% certain. In case of such an answer, a diagnostic test, such as a chorionic biopsy, amniocentesis, or a diagnostic test performed on the newborn's venous blood after birth, must confirm or rule out a chromosomal disease.
- MISSED PREGNANCY or TRIPLOIDIA
This result indicates that it may be a twin pregnancy, one of which has died, or the fetus may have triploidy syndrome.
Who Can Be Tested and When?
The Panorama test is designed for expectant women of all ages. It is appropriate for both single and twin pregnancies, whether the pregnancy was achieved through natural conception or assisted reproductive technology. The test can be administered once the pregnancy has reached at least 9 full weeks (9 weeks and 0 days). To determine the duration of your pregnancy, please use our pregnancy calculator.
The Panorama test can be provided:
- Both in singleton and twin pregnancy;
- In the case of IVF pregnancy,
- In the case of a singleton pregnancy, when conceived with the help of a donor egg,
- As a result of the OSCAR test, which is a screening test for chromosomal abnormalities, an increased risk of a chromosomal disease was found. This is a significant finding that may warrant further investigation with the Panorama test.
- If there was a history of Down, Edwards or Patau syndrome or triploidy during the previous pregnancy, the Panorama test can provide reassurance and peace of mind.
- If chorionic biopsy or amniocentesis is contraindicated due to the increased risk of miscarriage,
- If one or both parents have a balanced Robertsonian translocation, there is an increased risk of the fetus having Down or Patau syndrome. This is an important genetic risk factor to consider when deciding whether to undergo the Panorama test.
- Hereditary X-linked diseases in the family (to determine the gender of the fetus).
The Panorama test cannot be offered:
- If the pregnancy is less than nine weeks,
- If the fetus has a developmental defect detected by ultrasound examination or if NT > 3.0 mm*;
- In the case of twin pregnancy, if the mother has conceived with the help of a donor egg,
- In the case of a singleton pregnancy, if the mother has conceived using a donor egg, it is not possible to assess sex chromosome pathologies or triploidy**.
- In case of twin pregnancy, if one of the fetuses has died,
- In the case of triplets,
- If the mother has had a bone marrow transplant or received stem cell treatment.
* If the fetus has a developmental defect detected during ultrasound or if the NT is > 3.0 mm, we recommend a chorionic villus sampling, because the Panorama test cannot detect all gene and chromosome diseases that may occur in the fetus with an increased NT.
** In the case of IVF pregnancy, if the mother has become pregnant with a donor egg, the Prenatalsafe Karyo Plus test can be used.
When performing the Panorama test, there is also a small chance that your original sample will not produce any results. In this case, we recommend a repeat analysis of the venous blood, for which no additional charge is required. If the re-examination does not yield a result, rest assured that the money will be refunded.
Who will especially benefit from the Panorama test?
-
We preferably recommend the Panorama test for young women
The frequency of chromosomal diseases is influenced by the age of the woman. The older the expectant mother, the greater the risk of carrying a child with a chromosomal disorder. Conventional NIPT tests are more sensitive in identifying chromosomal diseases in older women, leading to more negative screening results for younger women. The Panorama test, however, offers a unique advantage. Its sensitivity in detecting chromosomal diseases is not influenced by the woman's age, making it a reliable and trustworthy option for all expectant mothers, whether they are young or older.
-
We preferably recommend the Panorama test for women who are expecting twins
In case of multiple pregnancies, congenital malformations and chromosomal diseases of the fetus occur more often. The Panorama test can be performed at a very early stage of pregnancy. This gives an opportunity already at an early stage of pregnancy to carry out a selective fetal reduction in the case of a developmental disorder unsuitable for life in one twin, increasing the chance of the healthy twin being born alive and healthy.
Monozygotic twins who share a single placenta are at increased risk of life-threatening twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. The Panorama test can distinguish monozygotic twins from dizygotic twins and evaluate both twins separately for chromosomal disorders. Therefore, it is the only test that can indicate which of the twins is sick and, if the family wishes, assess the gender of both twins separately. The Panorama test can be used in women who are carrying twins that share either one or two different placentas (monozygotic or dichorionic twins). -
We preferably recommend the Panorama test for overweight women
Overweight women typically have a lower concentration of fetal extracellular DNA in a blood test. However, the Panorama test is a reliable alternative, capable of assessing the extracellular DNA of the fetus even in a very small concentration in the mother's venous blood. This information is crucial, as it significantly reduces the chance of the laboratory being unable to perform the analysis due to the small amount of fetal DNA, thereby preventing test failure.
The Panorama test also reduces the risk of false negative results, where the test indicates the child is healthy, but the presence of the disease is revealed when the child is born. In cases where the fetal structures are not evaluable with the OSCAR test due to the thickness of the woman's abdominal lining, the Panorama test is a dependable screening test.
-
We preferably recommend the Panorama test for women who have become pregnant through artificial insemination
The Panorama test is the preferred screening test for chromosomal disorders in women who conceived through artificial insemination, as false-positive results with the OSCAR test, in this case, are more common than in women who conceived spontaneously.
-
We prefer the Panorama test to detect sex chromosome abnormalities
The Panorama test, with its superior accuracy in detecting sex chromosome abnormalities, empowers expectant parents and healthcare professionals with crucial knowledge. Combined anomalies of sex chromosomes are more common than those of Down syndrome, making this information particularly valuable.
Children with prenatally diagnosed sex chromosome abnormalities have been shown to have a more straightforward course of development than those diagnosed postnatally. This is a testament to the effectiveness of available treatment options, which include: speech, physical and/or occupational therapy, early educational intervention, hormone therapy. These options offer hope for a positive outcome.
What chromosomal disorders can I find when I do the Panorama test?
The Panorama test, a powerful tool in prenatal care, is used to gain insights into the fetus's genetic makeup and identify certain chromosomal diseases. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, 46 copies in each pair, and the first 22 pairs are numbered (1-22).
The last pair is the sex chromosomes. Girls have two X chromosomes, and boys have one X and one Y chromosome. Health and developmental problems occur when there are extra or missing chromosomes.
When a chromosome has an extra copy, meaning there are 3 copies instead of the usual 2, it's termed a trisomy. This can lead to health and developmental issues.
If one chromosome has no copy - 1 copy instead of 2 - it is called monosomy.
-
Trisomy 21
An extra copy of chromosome 21 causes it in the fetus, which is also called Down syndrome. The frequency of occurrence depends on the age of the woman. A 25-year-old woman has a risk of 1 in 1,000 live births. A woman in her 40s has a risk of 1 in 90 live births. It is an incurable chromosomal abnormality, one of the symptoms of which is mental retardation. Down syndrome is characterized by recognizable external features, short stature, low muscle tone, and excessive joint flexibility, and can be accompanied by heart defects and leukaemia. Some of the children die due to accompanying diseases or heart defects already in childhood, but the majority live to adulthood. Other medical conditions may also be present, including loss of hearing or vision.
-
Trisomy 18
It is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 18 in the fetus and is also called Edwards syndrome. The frequency of occurrence depends on the age of the woman. A 25-year-old woman has a risk of 1 in 5,000 live births. A woman in her 40s has a risk of 1 in 330 live births. It is an incurable chromosomal abnormality characterized by severe mental retardation. Most children with trisomy 18 have several severe congenital malformations of the brain, heart, and other organs. Intrauterine fetal growth retardation is common, and pregnancies often terminate or end in stillbirth. Most live-born children die before reaching one year of age, but 10% of children live beyond their first year of life. The surviving children have severe intellectual disabilities and growth and development problems.
-
Trisomy 13
An extra copy of chromosome 13 causes it, and it is also called Patau syndrome. The frequency of occurrence depends on the age of the woman. A 25-year-old woman has a risk of 1 in 10,000 live births. A woman in her 40s has a risk of 1 in 710 live births. It is an incurable chromosomal abnormality characterized by severe mental retardation. Most children with trisomy 13 have several severe developmental disorders of the brain, heart and other organs. Many pregnancies end in miscarriage and stillbirth. Most children born alive die before reaching one year of age.
-
Monosomy X
A sex chromosome abnormality in which females have only one X chromosome instead of two (45, X) is also called Turner syndrome. The frequency of occurrence does not depend on the woman's age and is 1 for every 2500 newborn girls. Children with Turner syndrome are shorter than average. They may have heart defects, kidney abnormalities, hearing problems and milder learning disabilities. They may require treatment with growth hormones in early childhood and usually require treatment with sex hormones during puberty. As adults, they are often infertile.
-
Klinefelter syndrome
A sex chromosome abnormality in which males have two X chromosomes instead of one (47, XXY). The frequency of occurrence does not depend on the woman's age. It is 1 for every 1000 newborn boys. Symptoms vary, and the condition is often not diagnosed until adulthood or goes undiagnosed. The most common symptom is infertility. Men with Klinefelter syndrome may be tall and have abnormal body proportions. They typically have small testicles and reduced testosterone production, leading to delayed or incomplete puberty, breast enlargement, decreased muscle mass and bone density, and decreased facial and body hair. Some individuals may have undescended testicles, a urethral opening on the underside of the penis or a small penis, learning disabilities or developmental delays.
-
Jacobs syndrome
A sex chromosome abnormality in which males have two Y chromosomes instead of one (47, XYY). Jacobs syndrome occurs in approximately 1:1000 newborn boys. Symptoms can vary, and many patients have mild or no symptoms, so they never receive a diagnosis or receive it until later in life. The condition is associated with tall stature and may include a large head, large teeth, flat feet, widely spaced eyes, and morbid spine curvature. There may be an increased risk of asthma, seizures, autism spectrum disorders, learning disabilities and behavioural problems. Fertility problems are slightly more common compared to the general population, but in most cases, fertility is normal
-
Trisomy X
A sex chromosome abnormality in which females have three X chromosomes instead of two (47, XXX). The incidence is approximately 1:1000 per newborn girl. The appearance of girls with trisomy X is variable, and most have no or mild symptoms. An estimated 10% of individuals with trisomy X are diagnosed. Standard features include tall stature, low muscle tone, and crooked fifth fingers. Other associated features include seizures, kidney problems, developmental delay, and learning disabilities. Sexual development and fertility are usually normal, but some women may experience fertility problems, abnormal ovarian and/or uterine development, premature ovarian failure, and early or late puberty.
-
Triploidy
If a fetus with a normal karyotype has 46 chromosomes, a fetus with triploidy syndrome has all three pairs of chromosomes, thus 69 chromosomes. Fetuses with this syndrome have pronounced early growth retardation with severe developmental defects often unsuitable for life, which is why fetuses with complete triploidy are stillborn or die in the very early postnatal period. A mother carrying a fetus with triploidy syndrome is more likely to have preeclampsia, severe nausea, and bleeding during pregnancy. The incidence is 1 in every 1,000 fetuses in the first trimester.
Before administering the Panorama test, we conduct an ultrasound examination to detect very early fetal developmental defects.
The Panorama test itself is designed to screen for certain chromosomal conditions, providing valuable information about the baby's health.
The ultrasound examination serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it provides specific details about the pregnancy, such as its size and the presence of a twin pregnancy. Secondly, it acts as a reassuring step, ruling out situations where the Panorama test should not be performed. Since the Panorama test cannot detect the child's structural-developmental defects, the ultrasound examination of the very early developmental defects of the fetus is designed to rule out 10 severe developmental defects, providing a sense of security.
For most women who undergo the Panorama test, the results bring a wave of relief. They find out that their baby has a low risk of developing the chromosomal condition tested for, which can be a source of hope and encouragement.
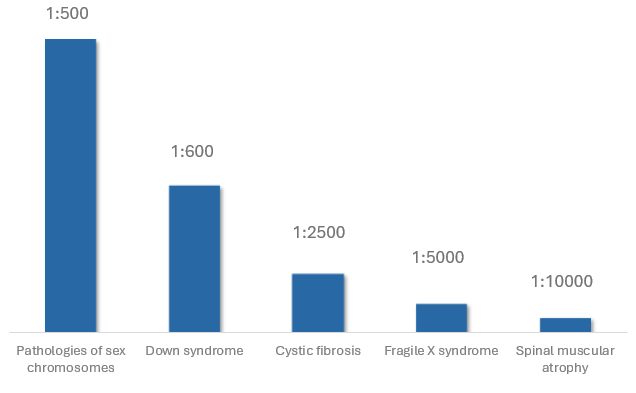
Tests for chromosomal and genetic diseases