Pregnancy week by week
| Selected week: |
You
Although it might take another week or two, it is not impossible in case of repeated pregnancy that you start feeling the movements of the fetus. There will be increasingly less room in the stomach and several inner organs are therefore pressed together. The pressure on the bladder makes you visit the toilet more and more often. Your body starts to produce more melanin and thus darker spots could appear on your body which recover only after birth. Also, the birthmarks on your skin might become darker. When you feel as if butterflies fly around your stomach, this could be the baby who kicks against the uterus wall. The new mothers might not perceive the activities of the child and it takes in any case a couple of weeks up to feeling the movements. However, with the fetal doppler, it is already possible to hear the baby's heartbeat.
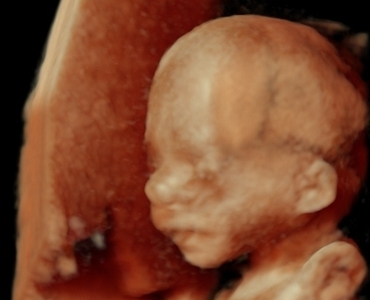
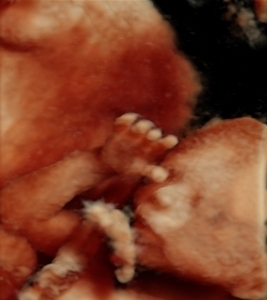
Your baby
Your baby weighs now about 250 g and is about 17 cm long. The baby is kicking, sleeping and swallowing. Its bones are becoming stronger. Its ears are almost at their correct place. The baby’s body has two layers of skin: epidermis and underskin tissue. The blood vessels are still transparent and the body is covered with fetal ointment.
Dr. Šois recommends
Due to the slow-down of the lower blood pressure and cardiovascular work you can feel dizzy or even faint. This is normal when it is not happening often, i.e. several times a day. At the same time you should pay attention to whether the mentioned symptoms appear very seldom and occur unexpectedly. Usually you feel dizzy after sudden change of the position, for example when you stand up abruptly. To avoid this, you should move peacefully.
The screening of fetal developmental abnormalities can be performed for the size of pregnancy of weeks 20-21.
What can we learn by performing the screening of fetal developmental abnormalities?
- Specification of the size of pregnancy and due date of birth
- In case of pre-eclampsia risk assessment of efficiency of prophylactic treatment
- Existence or absence of fetal growth restriction
- Existence or absence of fetal heart developmental abnormalities
- Existence or absence of pathology of fetal central nervous system
- Existence or absence of developmental abnormalities of other fetal organ structures
- Existence or absence of frontal position or in-growth of placenta into uterus
- Existence or absence of premature birth risk