Immunisation against rhesus incompatibility and hemolytic disease of the fetus
If the mother is RhD negative and the child is RhD positive, there may be a rhesus incompatibility in which the mother's immune system produces protein antibodies to protect the body against the child's red cells, causing the fetus to develop haemolytic disease. It is possible to assess foetal RhD in pregnancy using a non-invasive and foetal safe RhSafe test.
If the mother does not have anti-D antibodies, anti-RhD prophylaxis can be performed on the RhD-positive child at the 28th week of pregnancy. This is done by using anti-D immunoglobulin Rhesonativ, whose antibodies prevent the mother's body from developing antibodies and thereby developing haemolytic disease in the foetus.
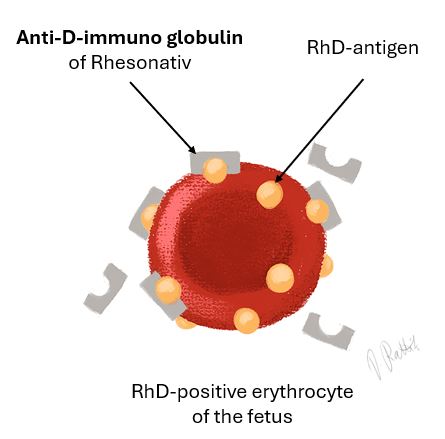
Figure: Rhesonativ's effect on blocking antibodies on the surface of red blood cells
Women who received Rhesonativ before the baby was born will receive a second dose of anti-D immunoglobulin within three days of delivery.
Figure: Effect of Rhesonativ in blocking antibodies on the surface of red blood cells
Rhesonativ is indicated in RhD-negative women who carry a RhD-positive child, in cases where there is a risk that the mother's and the child's blood may be exposed for some reason, such as pregnancy-related trauma, chorionic biopsy, fetal water exploration or an external foetal twist. A very small amount of RhD-positive blood is required to achieve immunity; 0.1 ml is sufficient. There is also spontaneous mixing of foetal and maternal blood during pregnancy, mainly after the 28th week of pregnancy (during the third trimester).
As with any medicine, there may be side effects when Rhesonativ is injected. Pain at the injection site, which can last from a few hours to a few days, is more common. In some cases, mild fever, headache or rash may occur. Very rarely, a pronounced allergic reaction may occur.
Rhesonativ may be co-administered with other vaccines recommended for pregnant women, such as a vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, whooping cough and tick encephalitis.
See: Vaccination during pregnancy
